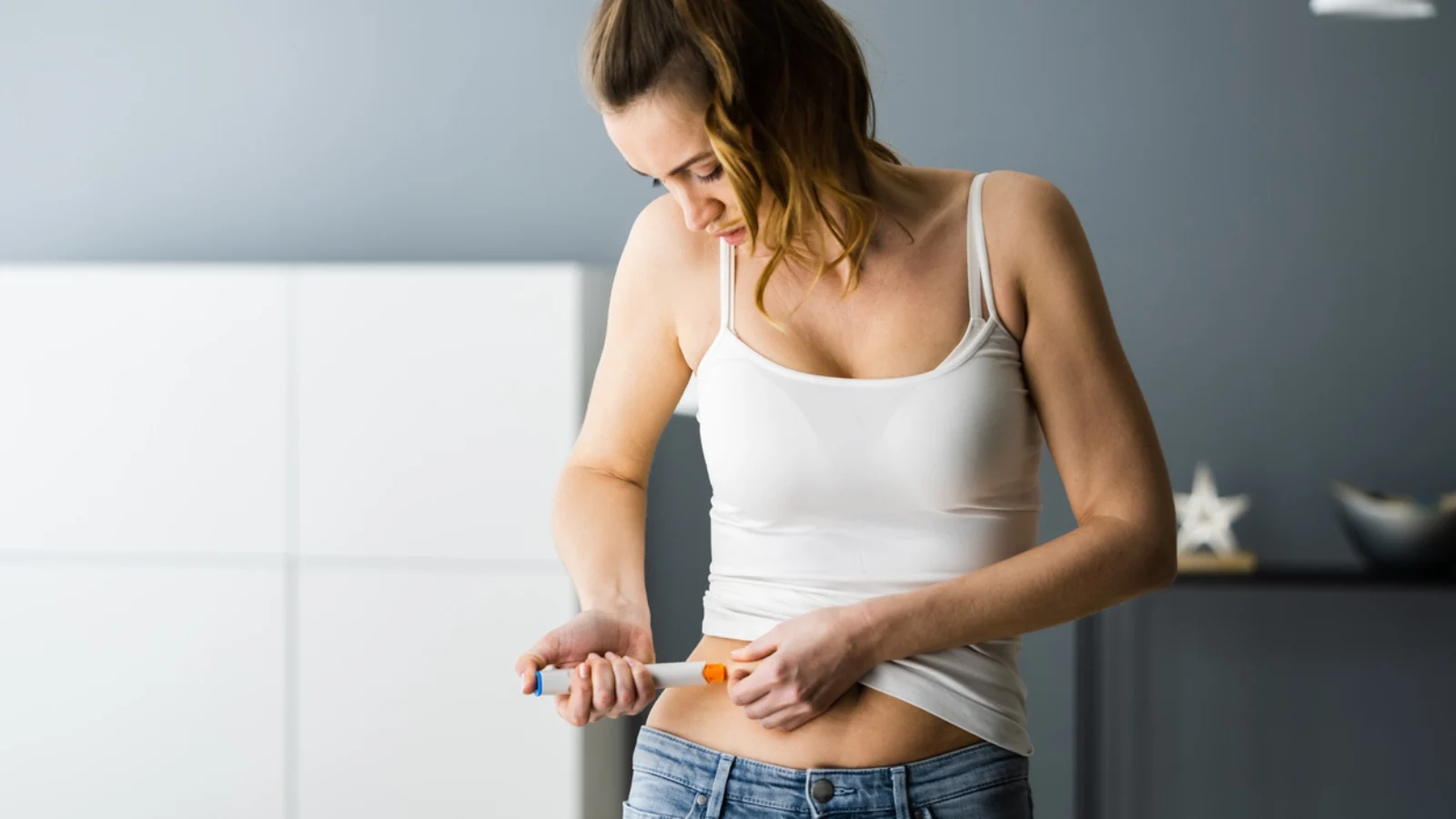
Can a Woman Self-Administer Fertility Drugs for IVF?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a journey filled with hope, questions, and sometimes a bit of nervousness—especially when it comes to fertility drugs. If you’re considering IVF or already on this path, you’ve probably wondered: Can I handle giving myself those shots? The short answer is yes, many women successfully self-administer fertility drugs at home as part of their IVF treatment. But there’s a lot more to it than just picking up a needle. Let’s dive into everything you need to know—how it works, what to expect, tips to make it easier, and even some fresh insights you might not find elsewhere.
This guide is here to walk you through the process step-by-step, answer your biggest questions, and give you practical advice to feel confident. Whether you’re worried about the pain, curious about the medications, or just want to know if you can do it solo, we’ve got you covered.
What Are Fertility Drugs in IVF, and Why Do They Matter?
IVF isn’t just about eggs and sperm meeting in a lab—it’s a carefully timed process that starts with your body. Fertility drugs are the key to making sure your ovaries produce enough eggs for the procedure. Think of them as the behind-the-scenes helpers that set the stage for success.
The Role of Fertility Drugs
These medications do a few big jobs:
-
- Stimulate your ovaries to grow multiple eggs (instead of the usual one per month).
-
- Control timing so your doctor can retrieve those eggs at the perfect moment.
-
- Support your body after the eggs are retrieved and embryos are transferred.
Without these drugs, IVF wouldn’t work the way it does. They’re like the fertilizer in a garden—helping you grow more “blooms” for the best chance at a healthy pregnancy.
Common Types of Fertility Drugs
Here’s a quick rundown of what you might encounter:
-
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Boosts egg growth. Brands like Gonal-F or Follistim are common.
-
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Works with FSH to mature those eggs. Often found in drugs like Menopur.
-
- GnRH Agonists/Antagonists: Prevents early ovulation. Think Lupron (agonist) or Cetrotide (antagonist).
-
- hCG Trigger Shot: Tells your ovaries to release the eggs. Ovidrel is a popular one.
-
- Progesterone: Prepares your uterus for the embryo. This might come as a shot, pill, or suppository.
Each drug has its own job, and most are given as injections you’ll do at home. Don’t worry—we’ll break down how that works later!
Why Self-Administering Matters
Doctors don’t usually give these shots in the office every day—it’d be a logistical nightmare! Instead, they teach you (or a partner) to do it yourself. This saves time, cuts costs, and gives you control over your treatment. Plus, with today’s easy-to-use injection pens, it’s less intimidating than it sounds.
Can You Really Do It Yourself? The Truth About Self-Administering
Yes, you can self-administer fertility drugs for IVF—and most women do! Studies show that over 90% of IVF patients manage their own injections with proper training. It’s normal to feel unsure at first, but with practice, it becomes second nature.
What Makes It Possible
-
- Simple Tools: Many drugs come in pre-filled pens or syringes, like using a marker instead of a paintbrush.
-
- Clear Instructions: Your clinic will give you step-by-step guidance, often with videos or hands-on demos.
-
- Support: Nurses are just a call away if you hit a snag.
Real Stories
Take Sarah, a 32-year-old teacher who did IVF last year. “I was terrified of needles,” she says. “But after my nurse showed me how to use the pen, I realized it wasn’t that bad. By day three, I was a pro!” Sarah’s not alone—thousands of women find that self-injecting isn’t as scary as they thought.
The Catch
It’s not for everyone. If you faint at the sight of needles or have shaky hands, you might need help from a partner or friend. The good news? Clinics are flexible and can adjust to what works for you.
How Does Self-Administering Fertility Drugs Work?
Let’s get into the nitty-gritty. Self-administering isn’t about guessing—it’s a structured process with clear steps. Here’s how it typically goes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Injecting Fertility Drugs
-
- Gather Supplies: You’ll need your medication, a syringe or pen, alcohol wipes, and a sharps container.
-
- Wash Up: Clean hands are a must to avoid infection.
-
- Prep the Dose: Follow your clinic’s instructions—some drugs need mixing, others are ready to go.
-
- Pick a Spot: Most shots go in your belly (around the navel) or thigh. Rotate sites to avoid soreness.
-
- Clean the Area: Swipe with an alcohol wipe and let it dry.
-
- Inject: Pinch the skin, insert the needle at a 90-degree angle, and press the plunger slowly.
-
- Finish Up: Pull out the needle, dispose of it safely, and press the spot with gauze if needed.
Subcutaneous vs. Intramuscular Injections
-
- Subcutaneous (Sub-Q): Into the fatty tissue under the skin. These are quick and use tiny needles—most IVF drugs are this type.
-
- Intramuscular (IM): Into the muscle, usually the buttock. Progesterone shots are often IM and sting more, so some women ask a partner to help.
Timing Is Everything
Your doctor will give you a schedule—say, FSH every evening at 8 PM for 10 days, followed by a trigger shot at exactly 11 PM. Timing matters because it syncs with your egg retrieval. Set reminders on your phone to stay on track!
What Does It Feel Like? Managing Pain and Side Effects
Let’s be real—nobody loves needles. But how bad is it, really? And what about side effects? Here’s what to expect.
The Injection Itself
-
- Pain Level: Most women say it’s a quick pinch, like a mosquito bite. Sub-Q shots are milder than IM ones.
-
- Tips to Ease It: Ice the spot beforehand, breathe deeply, or distract yourself with music.
“I tell my patients to think of it like popping a zit—it’s over before you know it,” says Orion Nightingale, a fertility nurse with 15 years of experience. “The anticipation is worse than the shot.”
Side Effects of Fertility Drugs
These meds can throw your hormones into overdrive. Common side effects include:
-
- Bloating: Your ovaries are working overtime!
-
- Mood Swings: Hormones can make you feel like you’re on an emotional rollercoaster.
-
- Tenderness: Injection sites might get sore or red.
-
- Headaches: A mild annoyance for some.
Rarely, a condition called Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) can occur, causing severe bloating or pain. Call your doctor ASAP if that happens—it’s treatable but serious.
Coping Strategies
✔️ Stay Hydrated: Helps with bloating.
✔️ Rest Up: Give your body a break.
❌ Don’t Panic: Mild discomfort is normal—reach out if it’s unbearable.
Pros and Cons of Self-Administering Fertility Drugs
Is it worth doing it yourself? Let’s weigh the good and the not-so-good.
Benefits
-
- Convenience: No daily clinic visits—do it at home on your schedule.
-
- Cost Savings: Fewer appointments mean lower bills.
-
- Empowerment: Taking charge can feel rewarding.
Challenges
-
- Learning Curve: It takes a few tries to get comfy.
-
- Nerves: Anxiety can make that first shot tricky.
-
- Mistakes: Mixing doses wrong or missing a time could mess with results.
A Fresh Take: The Mental Boost
Here’s something you won’t find in every article—self-administering might actually help your mindset. A 2023 study from the Journal of Fertility Psychology found that women who managed their own shots reported feeling 20% more in control of their IVF journey. That sense of ownership can reduce stress, which is huge when you’re already juggling so much.
Who Shouldn’t Self-Administer? Knowing Your Limits
Self-injecting isn’t a one-size-fits-all deal. Some women might need extra help—and that’s okay.
When to Get Assistance
-
- Needle Phobia: If you freeze up, ask a partner or friend.
-
- Physical Issues: Arthritis or poor vision can make it tough.
-
- Complex Protocols: If your doses change daily, a pro might step in.
Alternatives
-
- Partner Help: Many spouses learn to give the shots.
-
- Clinic Visits: Some women prefer a nurse to handle it.
-
- Home Nurse: In rare cases, insurance might cover this.
Top Tips for Self-Administering Like a Pro
Ready to ace those injections? These practical hacks—some classic, some new—will make it smoother.
Before You Start
✔️ Practice First: Ask your clinic for a saline demo.
✔️ Watch Videos: Online tutorials (from legit sources!) can boost confidence.
✔️ Organize: Lay out supplies in order so you’re not fumbling.
During the Shot
✔️ Go Slow: Rushing leads to mistakes.
✔️ Rotate Sites: Keeps skin happy—left belly one day, right thigh the next.
❌ Don’t Rub: Press gently instead to avoid irritation.
Aftercare
✔️ Track It: Log each shot (time, dose, site) in a notebook or app.
✔️ Chill Out: Reward yourself with tea or a show—self-care matters!
A Unique Tip: The “Buddy System”
Try syncing your injection time with a friend also doing IVF (virtually or in person). Chat while you prep—it’s like a mini support group. “I had a patient who FaceTimed her sister every night for shots,” says Ophelia, a reproductive health counselor. “They laughed through it, and it made a huge difference.”
Common Questions About Self-Administering Fertility Drugs
You’ve got questions—we’ve got answers. Let’s tackle the ones popping up all over Google (and some that should!).
Does It Hurt More Than a Flu Shot?
Not really! Sub-Q shots use smaller needles, so they’re often less painful. IM shots (like progesterone) can sting more, but numbing cream helps.
What If I Mess Up the Dose?
Call your clinic right away—they’ll fix it. Most mistakes (like a slightly off dose) won’t ruin your cycle, but timing is trickier to correct.
Can I Travel While Doing Shots?
Yes, with planning:
-
- Pack meds in a cooler (check TSA rules).
-
- Bring extra supplies.
-
- Stick to your schedule, even across time zones.
Are There New Tools Making It Easier?
Absolutely! In 2024, companies rolled out “smart pens” that beep to confirm the right dose. Ask your doctor if they’re available—they’re not everywhere yet, but they’re game-changers.
The Science Behind Self-Administering: What Studies Say
Let’s geek out for a sec—research backs up why this works. A 2022 study in Fertility and Sterility found that 95% of women trained to self-inject did so accurately after just one session. Error rates dropped to under 2% by week two. Why? Practice and good teaching.
Latest Data
-
- Success Rates: Self-administering doesn’t lower IVF success compared to clinic shots.
-
- Safety: Infection risk is near zero with proper hygiene.
-
- Comfort: Over 80% of women rate it “manageable” after a week.
This isn’t guesswork—it’s a proven system designed for you to succeed.
Busting Myths About Self-Administering Fertility Drugs
There’s a lot of noise out there. Let’s clear up some big misconceptions.
Myth #1: It’s Too Complicated
Truth: It looks tricky, but it’s like learning to ride a bike—awkward at first, then easy.
Myth #2: You’ll Hurt Yourself
Truth: Tiny needles and simple steps make it safe. Serious issues are super rare.
Myth #3: Only Nurses Should Do It
Truth: Nurses train you because you can do it—decades of IVF patients prove it.
The Emotional Side: How It Feels to Take Control
IVF is an emotional marathon, and self-injecting adds a layer. Some days, you’ll feel like a warrior; others, you might dread the needle. That’s normal.
Building Confidence
Each shot is a small win. “Patients often tell me they’re shocked at how strong they feel after a week,” says Caspian Sterling, a fertility specialist. “It’s a quiet kind of power.”
When It’s Tough
If you’re overwhelmed, talk to someone—a friend, therapist, or IVF support group. You’re not alone, even if it feels that way at 2 AM with a syringe in hand.
A New Angle: The Ritual Effect
Here’s a twist—turning injections into a ritual can help. Light a candle, play a favorite song, or say a little mantra (“I’ve got this”). Studies on routine and stress suggest this can lower anxiety by 15%. It’s not just a shot—it’s your moment.
What Happens After the Shots? The IVF Journey Continues
Self-administering is just one chapter. Here’s what’s next:
-
- Egg Retrieval: Done under sedation at the clinic—no shots involved.
-
- Embryo Transfer: A quick procedure, no needles here either.
-
- Progesterone: You might keep injecting this post-transfer to support pregnancy.
Your shots pave the way for these steps, so every pinch is worth it.
Tools and Tech: What’s New in 2025?
IVF keeps evolving, and 2025 brings cool updates:
-
- Wearable Monitors: Devices that track hormone levels and suggest dose tweaks.
-
- Needle-Free Options: Early trials of nasal sprays for some drugs—fingers crossed!
-
- Apps: Tools like “IVF Buddy” remind you when to inject and log your progress.
These aren’t standard yet, but they’re hints of an easier future.
Your Support Squad: Who’s Got Your Back?
You don’t have to go it alone. Here’s who can help:
-
- Clinic Team: Nurses and docs are your first call.
-
- Partner/Family: They can inject or just cheer you on.
-
- Online Communities: Forums like Reddit’s r/IVF are goldmines for tips.
Let’s Talk: Your Turn!
Self-administering fertility drugs for IVF is a big deal, but it’s doable—and you’re tougher than you think. What’s your biggest worry about it? Or if you’ve done it, what’s your best tip? Drop a comment below—I’d love to hear your story! And if this helped, share it with someone else starting their IVF adventure.