Mastering Ovarian Stimulation Protocols: Your Guide to IVF Success
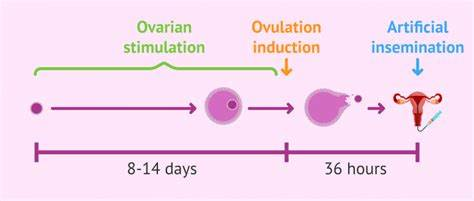
Ovarian stimulation is the heartbeat of IVF (in vitro fertilization). It’s the process where medications are used to encourage your ovaries to produce multiple eggs, giving you the best shot at a successful pregnancy. But with so many different protocols—like the long agonist, short antagonist, and mild stimulation—it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. Which one is right for you? How do you minimize side effects? And what can you do to boost your chances of success?
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about ovarian stimulation protocols. We’ll go beyond the basics, offering you a deeper understanding, practical tips, and even a fun quiz to help you figure out which protocol might be best for your situation. Whether you’re just starting your fertility journey or looking to optimize your next cycle, this article is your roadmap to making informed decisions.
Understanding Different Ovarian Stimulation Protocols
Ovarian stimulation protocols are like recipes—each one uses a unique mix of medications, timing, and techniques to help your ovaries produce multiple eggs. Let’s explore the most common protocols, who they’re best for, and what makes each one different.
Long Agonist Protocol
What It Is: The long agonist protocol is one of the oldest and most widely used. It starts with a medication called a GnRH agonist to “quiet” your pituitary gland, preventing it from releasing hormones too early. After about 10-14 days, you begin taking gonadotropins to stimulate your ovaries.
Medications Used: GnRH agonist (like Lupron), gonadotropins (like Gonal-F or Follistim), and a trigger shot (hCG or Lupron).
Timeline: Around 4-5 weeks from start to egg retrieval.
Best For: Women with a normal ovarian reserve, especially those under 35.
Pros:
✔️ High egg yield
✔️ Lower risk of premature ovulation
Cons:
❌ Longer treatment time
❌ More injections
Short Antagonist Protocol
What It Is: This protocol is faster and involves fewer injections. You start with gonadotropins right away, and after a few days, a GnRH antagonist is added to prevent early ovulation.
Medications Used: Gonadotropins, GnRH antagonist (like Ganirelix or Cetrotide), and a trigger shot.
Timeline: About 2-3 weeks from start to egg retrieval.
Best For: Women over 35, those with a lower ovarian reserve, or those who want a shorter protocol.
Pros:
✔️ Shorter duration
✔️ Fewer injections
Cons:
❌ Slightly higher risk of premature ovulation
❌ May yield fewer eggs in some cases
Mild Stimulation Protocol
What It Is: Also known as “mini IVF,” this protocol uses lower doses of medications, often combining oral drugs like clomiphene with small amounts of gonadotropins.
Medications Used: Clomiphene or letrozole, low-dose gonadotropins, and a trigger shot.
Timeline: Similar to the short antagonist protocol, around 2-3 weeks.
Best For: Women with a low ovarian reserve, those sensitive to medications, or those looking to reduce costs.
Pros:
✔️ Lower medication doses (and costs)
✔️ Fewer side effects
Cons:
❌ Fewer eggs retrieved
❌ May not be ideal for women who need multiple embryos
Other Emerging Protocols
Newer protocols, like the duo-stim (double stimulation in one cycle) and microdose flare, are gaining attention, especially for women with diminished ovarian reserve. These protocols aim to maximize egg production in challenging cases.
Expert Insight: “Emerging protocols like duo-stim are showing promise for patients with diminished ovarian reserve, offering new hope for those who previously had limited options,” says Caspian Sterling, an expert in fertility preservation.
Medications Used in Ovarian Stimulation
Think of ovarian stimulation like gardening. Your ovaries are the soil, and the medications are like fertilizer and water. The goal is to grow multiple healthy follicles (flowers), but you have to be careful not to overdo it and cause a weed infestation (a condition called OHSS, which we’ll discuss later).
Gonadotropins
Role: These are the main “fertilizers” that stimulate your ovaries to produce multiple follicles. Common brands include Gonal-F, Follistim, and Menopur.
How They’re Taken: Daily injections, usually for 8-12 days.
Side Effects: Bloating, mood swings, and injection site discomfort.
GnRH Agonists and Antagonists
Role: These medications prevent your pituitary gland from triggering ovulation too early. Agonists (like Lupron) are used in long protocols, while antagonists (like Ganirelix) are used in short protocols.
How They’re Taken: Injections, starting at different points depending on the protocol.
Side Effects: Headaches, hot flashes, and fatigue.
Trigger Shots
Role: The final step before egg retrieval, the trigger shot helps your eggs mature so they’re ready for fertilization. It can be hCG or a GnRH agonist like Lupron.
Timing: Given precisely 36 hours before egg retrieval.
Side Effects: Mild cramping or bloating.
Monitoring Your Ovarian Stimulation Cycle
Monitoring is like checking on your garden every day to see how the plants are growing. Through ultrasounds and blood tests, your doctor tracks how your follicles are developing and adjusts your medications as needed.
-
- Ultrasounds: Measure follicle size and count.
-
- Blood Tests: Check hormone levels, especially estrogen.
What to Expect: You’ll have 4-6 monitoring appointments during your cycle. Each visit helps ensure you’re on track for a successful egg retrieval.
Expert Insight: “Close monitoring during stimulation allows us to adjust medications in real-time, optimizing egg quality and quantity,” explains Ophelia, a renowned reproductive endocrinologist.
Trigger Shots and Egg Retrieval
The trigger shot is the signal that it’s time to “harvest” your eggs. Timing is everything—too early, and the eggs won’t be mature; too late, and you might ovulate before retrieval.
-
- Types of Trigger Shots: hCG is the most common, but for women at risk of OHSS, a GnRH agonist like Lupron might be used.
-
- Egg Retrieval: A minor surgical procedure where eggs are collected from your ovaries using a thin needle guided by ultrasound.
Risks and Side Effects of Ovarian Stimulation
While ovarian stimulation is generally safe, it’s important to be aware of potential risks.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
OHSS occurs when your ovaries overreact to the medications, leading to swelling and fluid buildup. It’s like overwatering your garden, causing the plants to drown.
-
- Symptoms: Bloating, abdominal pain, nausea.
-
- Prevention: Lower medication doses, using a GnRH agonist trigger, or freezing all embryos instead of doing a fresh transfer.
Multiple Pregnancies
Stimulation can lead to multiple eggs being fertilized, increasing the chance of twins or more.
-
- Risk: Higher chance of complications like preterm birth.
-
- Prevention: Single embryo transfer (SET) is often recommended.
Other Potential Complications
Rarely, ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary) or infection can occur. Always report severe pain or unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Choosing the Right Protocol for You
Selecting the best protocol is like finding the perfect recipe for your unique garden. Your doctor will consider several factors:
-
- Age: Younger women may respond better to standard protocols, while older women might need more tailored approaches.
-
- Ovarian Reserve: Measured by tests like AMH or antral follicle count (AFC).
-
- Previous Responses: If you’ve had IVF before, how you responded can guide future protocols.
Interactive Quiz: Find Your Protocol
Answer these questions to get a sense of which protocol might be suitable for you. (Remember, this is not medical advice—always consult your fertility specialist.)
-
- What is your age?
a. Under 35
b. 35-40
c. Over 40
- What is your age?
-
- How would you describe your ovarian reserve?
a. Normal
b. Diminished
c. High (e.g., PCOS)
- How would you describe your ovarian reserve?
-
- Have you had previous IVF cycles?
a. No
b. Yes, with good response
c. Yes, with poor response
- Have you had previous IVF cycles?
Based on your answers:
-
- Mostly A’s: You might be a candidate for the long agonist or short antagonist protocol.
-
- Mix of A’s and B’s: Consider the short antagonist or mild stimulation protocol.
-
- Mostly C’s: Specialized protocols like duo-stim or microdose flare could be options.
Latest Research and Innovations in Ovarian Stimulation
Fertility science is always evolving. Here are some exciting developments:
-
- Letrozole for Estrogen-Sensitive Patients: Recent studies show that combining letrozole (an oral medication) with gonadotropins can reduce estrogen levels while still stimulating follicle growth. This is especially helpful for women with breast cancer or those sensitive to estrogen.
-
- Duo-Stim Protocol: This approach involves two rounds of stimulation in a single cycle, which can be a game-changer for women with low ovarian reserve.
Expert Insight: “The choice of ovarian stimulation protocol should be tailored to each patient’s unique profile. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach in IVF,” says Dr. Orion Nightingale, a leading fertility specialist.
Patient Stories: Real Experiences with Ovarian Stimulation
Hearing from others who’ve been through it can be incredibly reassuring. Here are two brief stories:
-
- Sarah, 32: “I did the short antagonist protocol and got 15 eggs, which turned into 8 embryos. I loved that it was quick and didn’t require as many shots.”
-
- Emily, 38: “After two failed cycles, I tried the microdose flare protocol. I only got 5 eggs, but 2 became embryos, and now I’m pregnant with my first child.”
Financial Considerations of Ovarian Stimulation Protocols
Cost is a big concern for many families. Here’s a rough comparison of protocol costs (note: prices vary widely):
| Protocol | Average Medication Cost | Monitoring Visits | Total Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long Agonist | $3,000 – $5,000 | 5-7 | $4,000 – $6,000 |
| Short Antagonist | $2,500 – $4,000 | 4-6 | $3,500 – $5,000 |
| Mild Stimulation | $1,500 – $3,000 | 3-5 | $2,500 – $4,000 |
Always ask your clinic for a personalized quote, and check if your insurance covers any part of the treatment.
Lifestyle Tips for Optimizing Ovarian Stimulation
Your daily habits can impact your stimulation cycle. Here’s how to set yourself up for success:
-
- Diet: Focus on a Mediterranean-style diet with plenty of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins. Some studies suggest CoQ10 supplements may improve egg quality.
-
- Exercise: Stick to low-impact activities like walking or yoga. Avoid high-intensity workouts that could strain your ovaries.
-
- Stress Management: Try mindfulness, acupuncture, or joining a support group. It’s okay to ask for help!
Frequently Asked Questions
-
- Can I have sex during ovarian stimulation?
It’s generally safe, but your doctor might advise against it if your ovaries are very enlarged.
- Can I have sex during ovarian stimulation?
-
- What if I miss a dose of medication?
Call your clinic immediately for instructions. Don’t double up on doses.
- What if I miss a dose of medication?
-
- How many eggs should I aim for?
Ideally, 15-20 mature eggs, but quality matters more than quantity.
- How many eggs should I aim for?
Conclusion
Ovarian stimulation is a complex but essential part of IVF. By understanding the different protocols, medications, and what to expect, you can feel more confident and in control of your fertility journey. Remember, every person’s situation is unique, so work closely with your fertility specialist to choose the protocol that’s right for you.
Interactive Content: Share Your Story
Have you gone through ovarian stimulation? What protocol did you use, and how was your experience? Share your story in the comments below to help others on their journey!

No comment