What Is Precycle Screening for IVF?
If you’re thinking about in vitro fertilization (IVF), you’ve probably heard the term “precycle screening” thrown around. But what does it really mean? Imagine it like the prep work before a big game—you wouldn’t step onto the field without warming up, right? Precycle screening is the warm-up for IVF, a series of tests and checks to make sure your body (and your partner’s) is ready for the journey ahead. It’s all about boosting your chances of success while keeping things safe and smooth.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into what precycle screening is, why it matters, and how it sets the stage for IVF. We’ll break it down step-by-step, answer your burning questions, and even sprinkle in some fresh insights you won’t find everywhere else. Whether you’re just curious or actively planning your IVF journey, stick around—this is everything you need to know, written just for you.
What Does Precycle Screening Mean?
Precycle screening is a set of medical tests and evaluations done before you start an IVF cycle. Think of it as a health checklist for you and your partner. Doctors use it to figure out how fertile you are, spot any issues that might get in the way, and tailor the IVF process to fit your unique needs. It’s not a one-size-fits-all deal—everyone’s body is different, and this step helps make sure the plan works for you.
Why It’s a Big Deal
IVF isn’t cheap or simple. It’s a big commitment—emotionally, physically, and financially. Precycle screening helps doctors catch problems early, so you don’t waste time or money on a cycle that’s doomed from the start. For example, if there’s an infection or a hormone imbalance, they can fix it before the real action begins. It’s like tuning up a car before a cross-country road trip—you want everything running smoothly.
What’s Included?
Here’s a quick rundown of what precycle screening might involve:
-
- Blood tests: Checking hormone levels like FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), LH (luteinizing hormone), and estrogen.
-
- Ultrasound: A peek at your ovaries and uterus to see what’s going on inside.
-
- Semen analysis: For the guys, this checks sperm count, movement, and shape.
-
- Infectious disease screening: Tests for things like HIV, hepatitis, or syphilis to keep everyone safe.
-
- Uterine evaluation: Making sure the womb is ready to welcome an embryo.
Each test has a job, and together, they paint a picture of your reproductive health. It’s all about setting up the best shot at a healthy pregnancy.
Why Precycle Screening Matters for IVF Success
You might be wondering, “Do I really need all these tests?” The short answer: Yes! Precycle screening isn’t just busywork—it’s a game-changer. Let’s break down why it’s so important.
Boosting Your Odds
IVF success rates aren’t 100% (sorry, no magic wand here!). For women under 35, the chance of a live birth per cycle is about 45%, according to 2021 data from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. That number drops as you get older. Precycle screening helps stack the deck in your favor by spotting and fixing issues that could lower those odds.
For instance, if your hormone levels are off, meds can balance them out. If there’s a cyst on your ovary, doctors can deal with it before starting IVF. Orion Nightingale, a fertility specialist, puts it this way: “Precycle screening is like a roadmap—it shows us where the potholes are so we can steer around them.”
Avoiding Heartbreak
Imagine going through weeks of injections, egg retrieval, and embryo transfer, only to find out your uterus can’t support a pregnancy because of something fixable. That’s a gut punch no one wants. Precycle screening catches those surprises early, saving you from unnecessary stress and disappointment.
Personalizing Your Plan
No two IVF journeys are the same. Maybe you’ve got a low egg count, or your partner’s sperm needs a little help. Precycle screening gives your doctor the info they need to tweak the process—whether that’s adjusting meds, timing things differently, or adding extra steps like genetic testing.
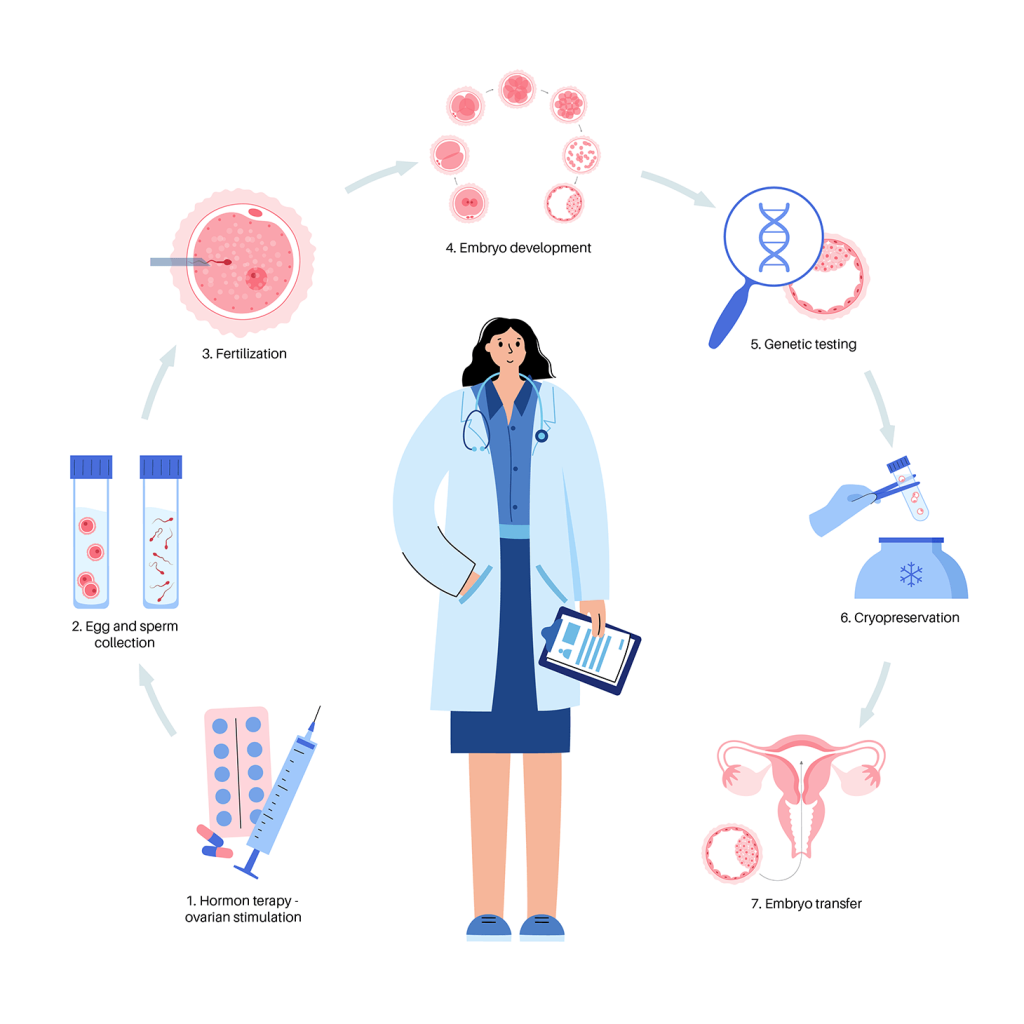
The Step-by-Step Process of Precycle Screening
Ready to see how this all works? Here’s a breakdown of what happens during precycle screening, step by step. Think of it as your backstage pass to the IVF prep show.
Step 1: The First Chat
It all starts with a visit to your fertility doctor. You’ll talk about your medical history—things like past pregnancies, surgeries, or health conditions. Be honest! Even small details (like that time you had irregular periods) can matter.
Step 2: Blood Work Bonanza
Next up: blood tests. You’ll get a little poke to check your hormone levels. These tests usually happen early in your menstrual cycle (day 2 or 3) because that’s when your hormones are at their “baseline.” Here’s what they’re looking for:
-
- FSH and LH: These control egg growth.
-
- Estradiol: A type of estrogen that affects your ovaries.
-
- AMH (anti-Müllerian hormone): A clue about how many eggs you’ve got left.
-
- Thyroid hormones: Because your thyroid can mess with fertility if it’s out of whack.
Step 3: Ultrasound Peek
Time for an ultrasound! This isn’t the belly kind you see in pregnancy movies—it’s a transvaginal ultrasound (yep, a wand goes inside). It checks:
-
- The number of follicles (egg sacs) in your ovaries.
-
- The size and shape of your uterus.
-
- Any cysts or fibroids that might cause trouble.
Step 4: Sperm Check
If you’ve got a male partner, they’re not off the hook. A semen analysis looks at sperm count, motility (how well they swim), and morphology (their shape). Fun fact: About 40% of infertility cases involve male factors, so this step is just as crucial.
Step 5: Safety First
Both partners get screened for infectious diseases. This protects you, your partner, and any future baby. Tests might include:
-
- HIV
-
- Hepatitis B and C
-
- Syphilis
Some clinics also check for rubella immunity or genetic conditions like cystic fibrosis if there’s a family history.
Step 6: Uterine Deep Dive
Finally, your doctor might do a hysterosalpingogram (HSG) or hysteroscopy. These are fancy ways of saying they’ll check your uterus and fallopian tubes to make sure they’re clear and healthy. An HSG uses dye and an X-ray, while a hysteroscopy uses a tiny camera.
How Long Does It Take?
The whole process usually takes a few weeks, depending on your cycle and how fast the lab works. Once it’s done, your doctor reviews everything and builds your IVF plan.
Common Questions About Precycle Screening
Let’s tackle some FAQs that pop up when people dive into precycle screening. These are the things you’re probably wondering about right now!
Does It Hurt?
Most of it? Not really. Blood tests are just a quick pinch, and the ultrasound might feel weird but isn’t painful. The HSG can be crampy for a few minutes, but it’s over fast. Think of it like a short workout—uncomfortable, but doable.
How Much Does It Cost?
Costs vary big time. In the U.S., precycle screening can run anywhere from $500 to $2,000, depending on your clinic and insurance. Some plans cover it, some don’t—so check with your provider. It’s a small chunk compared to IVF itself (which averages $15,000 per cycle), but it’s still worth budgeting for.
What If They Find Something Wrong?
Don’t panic! Finding an issue is the whole point—it means they can fix it. Maybe you need a quick surgery for a cyst, or a med tweak for hormones. Ophelia, a reproductive nurse, says, “A ‘problem’ in precycle screening isn’t a dead end—it’s a detour to a better outcome.”
Can I Skip It?
Technically, no. Most clinics require precycle screening—it’s standard practice to keep things safe and effective. Skipping it would be like baking a cake without preheating the oven. Sure, you could try, but the results might flop.
What the Latest Research Says
Precycle screening isn’t stuck in the past—it’s evolving with new science. Here’s what’s fresh in 2025, based on the latest studies and trends.
AMH Is a Star Player
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) is getting more attention. A 2024 study in Fertility and Sterility found that women with AMH levels below 1 ng/mL had a 20% lower IVF success rate. Why? Low AMH means fewer eggs, so doctors might push for egg donation or adjust your meds if your levels are low.
Genetic Screening Is on the Rise
Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) isn’t always part of precycle screening, but it’s becoming more common as an add-on. A 2023 Stanford Medicine study showed that screening embryos for genetic issues (like sickle cell disease) could cut long-term healthcare costs by millions. It’s not cheap upfront, but it’s a game-changer for some families.
Thyroid Matters More Than We Thought
New research from 2024 links thyroid function to IVF success. Women with even mild thyroid issues (like subclinical hypothyroidism) had a 15% lower implantation rate. Doctors are now pushing for tighter thyroid checks during precycle screening—something to ask about if it’s not on your list.
Precycle Screening Do’s and Don’ts
Want to ace your precycle screening? Here’s a handy guide to keep you on track.
✔️ Do These
-
- Prep your body: Eat well, sleep enough, and cut back on caffeine or alcohol a few weeks before. A healthy body gives better results.
-
- Ask questions: Not sure why you’re doing a test? Speak up! Your doctor’s there to help.
-
- Bring your partner: If you’ve got one, they need to be part of this too—especially for semen analysis.
-
- Track your cycle: Knowing your period dates helps time the tests right.
❌ Don’t Do These
-
- Stress out: Easier said than done, but stress can mess with your hormones. Try yoga or a chill playlist.
-
- Skip appointments: Missing a test could delay your IVF start date.
-
- Hide stuff: Forgot to mention that old surgery? Tell your doctor—every detail counts.
-
- Overdo it: Don’t start crazy diets or supplements without checking with your doc first.
Real-Life Stories: What Precycle Screening Looks Like
Let’s make this real with a couple of examples. These aren’t just facts—they’re people like you navigating the process.
Sarah’s Story
Sarah, 32, was pumped to start IVF. Her precycle screening showed a low AMH level—her egg count was lower than expected. Her doctor adjusted her meds to boost egg production, and after one cycle, she got pregnant. “I was freaked out at first,” she says, “but knowing the problem helped us solve it.”
Mike and Jamie’s Journey
Mike, 38, and Jamie, 36, hit a snag when his semen analysis showed slow-moving sperm. Precycle screening caught it early, and their clinic suggested a technique called ICSI (where sperm is injected right into the egg). Nine months later, they welcomed twins. “It was a hiccup we didn’t see coming,” Jamie admits, “but it worked out.”
These stories show how precycle screening isn’t just tests—it’s a tool to turn challenges into wins.
Precycle Screening vs. Other Fertility Tests
Confused about how precycle screening fits with other fertility stuff? Let’s clear it up with a comparison.
| Test Type | When It Happens | What It Checks | IVF Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precycle Screening | Before IVF starts | Hormones, sperm, uterus, infections | Sets up your IVF plan |
| Basic Fertility Workup | Before deciding on IVF | Initial infertility causes | Might lead to IVF or other fixes |
| PGS (Genetic Screening) | During IVF, after eggs retrieved | Embryo genetics | Optional add-on, not precycle |
Key Difference: Precycle screening is specific to IVF prep, while other tests might happen earlier or later in your fertility journey.
Tips to Make Precycle Screening Easier
This process can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to. Here are some practical hacks to breeze through it.
1. Build a Support Squad
Tell a friend or family member what’s up—they can cheer you on or tag along to appointments. Everything’s less scary with a buddy.
2. Keep a Notebook
Jot down test dates, results, and questions. It’s your personal IVF playbook—no more forgetting what the doctor said!
3. Chill Out (For Real)
Stress messes with hormones, and precycle screening needs accurate readings. Try this 5-minute trick:
-
- Sit quietly.
-
- Breathe in for 4 seconds, out for 4.
-
- Repeat until you feel calmer.
4. Budget Smart
Ask your clinic for a cost breakdown upfront. Some offer payment plans—don’t be shy about asking. Caspian Sterling, a fertility coach, advises, “Treat precycle screening like an investment—spend now to save heartache later.”
The Hidden Benefits of Precycle Screening
Most folks talk about how precycle screening boosts IVF success, but there’s more to it. Here are some perks you might not have thought of.
Peace of Mind
Knowing your body’s ready (or getting there) takes a huge weight off. It’s like checking the weather before a picnic—you feel more in control.
Health Bonus
Those blood tests might catch stuff beyond fertility—like a thyroid issue or vitamin D dip. Fixing those can make you feel better overall, not just for IVF.
Teamwork Vibes
If you’ve got a partner, doing this together builds trust and closeness. You’re in it as a duo, tackling each step side by side.
What Happens After Precycle Screening?
Once the tests are done, what’s next? Here’s the rundown.
Results Review
Your doctor sits you down (or Zooms you) to go over everything. They’ll explain what’s good, what needs work, and how it shapes your IVF plan.
Fixes First
If something’s off—like a cyst or low sperm count—they’ll handle it before moving forward. This might mean meds, a minor procedure, or just waiting a cycle.
Green Light
When everything checks out, you get the go-ahead. That’s when the real IVF fun starts: meds, egg retrieval, and all that jazz.
Let’s Talk: Your Turn!
Precycle screening might sound like a lot, but it’s your first big step toward building a family. Got questions? Thoughts? Drop them below—we’d love to hear from you! Here are a couple of prompts to get you started:
-
- What’s the one thing you’re most curious about with precycle screening?
-
- If you’ve done it, what surprised you the most?
Your story could help someone else feel less alone on this wild ride. Let’s chat!


