Follicular Abnormalities Affect Conception and IVF: What You Need to Know
When you’re trying to start a family, every step of the process feels important. For many, conception happens naturally, but for others, challenges like follicular abnormalities can make things tricky. Whether you’re hoping to conceive on your own or exploring in vitro fertilization (IVF), understanding how follicular abnormalities affect your journey is key. This article dives deep into what follicular abnormalities are, how they impact your chances of getting pregnant, and what you can do about them. We’ll break it down step by step, share the latest research, and offer practical tips to help you feel more in control.
What Are Follicular Abnormalities?
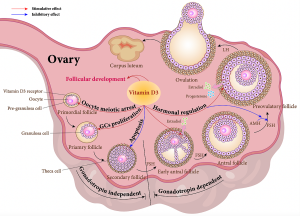
Follicles are tiny sacs in your ovaries where eggs grow. Each month, a healthy follicle matures and releases an egg during ovulation. But sometimes, things don’t go as planned. Follicular abnormalities happen when these sacs don’t develop properly, affecting egg quality, ovulation, or even how well IVF works.
Think of follicles like little nurseries for your eggs. If the nursery isn’t built right—maybe it’s too small, too big, or doesn’t open when it should—the egg inside might not be ready for action. These issues can range from minor hiccups to bigger roadblocks, and they’re more common than you might think.
Types of Follicular Abnormalities
- Poor Follicle Growth: The follicle doesn’t get big enough to release a healthy egg.
- Premature Ovulation: The follicle releases the egg too early, before it’s fully mature.
- Empty Follicles: The sac looks normal but has no egg inside (common in some IVF cases).
- Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that can mess up the ovulation process.
- Irregular Follicle Size: Some grow too fast, others lag behind, throwing off timing.
Why Should You Care?
Follicular abnormalities don’t just affect natural conception—they can also lower IVF success rates. If the follicles aren’t doing their job, the eggs retrieved during IVF might not be viable, or there might not be enough of them. Let’s explore how this plays out.
How Follicular Abnormalities Affect Natural Conception
Getting pregnant naturally depends on a perfect chain of events: a healthy follicle grows, releases a mature egg, and that egg meets sperm at just the right time. When follicular abnormalities step in, it’s like a glitch in the system.
The Science Behind It
Research shows that follicles need to reach about 18-25 millimeters in size to release a mature egg. If they’re too small or grow unevenly, the egg might not be ready. A 2022 study from Columbia University found that abnormal follicle development often ties back to hormonal imbalances—like too much or too little follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)—which can stop ovulation altogether.
Real-Life Impact
Imagine you’re baking cookies. If the oven doesn’t heat up enough, the dough won’t turn into delicious treats. Similarly, if a follicle doesn’t mature properly, the egg won’t be ready for fertilization. For some, this means irregular periods or no ovulation at all—both big hurdles to conception.
Signs You Might Have a Problem
✔️ Irregular periods (super long or super short cycles)
✔️ Painful cramps that feel unusual
✔️ No signs of ovulation (like changes in cervical mucus)
❌ Assuming every missed period means pregnancy—sometimes it’s a follicle issue!
What You Can Do
- Track Ovulation: Use ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) to see if you’re ovulating regularly.
- Talk to a Doctor: A simple ultrasound can check how your follicles are growing.
- Lifestyle Tweaks: Stress and poor diet can mess with hormones—more on this later!
Follicular Abnormalities and IVF: A Deeper Dive
IVF is like a high-tech workaround for conception challenges, but follicular abnormalities can still throw a wrench in the process. During IVF, doctors use medications to stimulate your ovaries to grow multiple follicles at once. The goal? Harvest as many healthy eggs as possible. But when follicles don’t cooperate, it’s a different story.
How It Works in IVF
In a typical IVF cycle:
- You take hormone shots to boost follicle growth.
- Doctors monitor your follicles with ultrasounds.
- When they’re ready (usually 18-20 mm), they trigger ovulation.
- Eggs are retrieved and fertilized in a lab.
If follicles grow unevenly, don’t mature, or turn out empty, you might end up with fewer eggs—or none at all. A 2023 study from Johns Hopkins University found that nearly half of IVF embryos fail due to early developmental issues linked to abnormal follicles.
Common IVF Challenges
- Low Egg Yield: Fewer follicles mean fewer eggs to work with.
- Poor Egg Quality: Abnormal follicles often produce eggs that don’t fertilize well.
- Empty Follicle Syndrome: A rare but frustrating issue where no eggs are retrieved despite good-looking follicles.
Quick Stats
- Normal IVF cycle: 8-15 eggs retrieved.
- With follicular issues: Sometimes as few as 1-3 eggs, or none.
A Patient’s Story
Take Sarah, a 34-year-old who tried IVF twice. Her first cycle yielded only two eggs because most of her follicles were too small. After adjusting her meds and diet, her second cycle produced eight eggs—four became healthy embryos. Follicular abnormalities don’t always mean failure, but they do need extra attention.
What Causes Follicular Abnormalities?
So, why do follicles go rogue? It’s not just bad luck—several factors can play a role. Understanding these can help you and your doctor figure out the best plan.
Hormonal Imbalances
- High FSH: Pushes follicles too hard, too fast.
- Low Estrogen: Slows growth, leaving follicles underdeveloped.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Causes lots of small follicles but few mature ones.
Age and卵巢储备 (Ovarian Reserve)
As you get older, your ovarian reserve—the number of eggs left—drops. A 2024 study from Yale Medicine showed that women over 35 often have more irregular follicle growth, even with IVF stimulation.
Lifestyle Factors
- Stress: Raises cortisol, which can disrupt hormone signals.
- Weight: Being under or overweight affects follicle development.
- Smoking: Toxins damage follicles and eggs alike.
Mini Quiz: Are You at Risk?
Answer yes or no:
- Are you over 35?
- Do you have irregular periods?
- Do you smoke or live with a smoker? If you said “yes” to two or more, talk to a doctor about your follicles!
Diagnosing Follicular Abnormalities
Wondering if this applies to you? Diagnosis is the first step to getting answers. Here’s how it works.
Tools Doctors Use
- Ultrasound: Sees follicle size and count in real time.
- Blood Tests: Checks FSH, estrogen, and other hormone levels.
- HSG (Hysterosalpingogram): Rules out blockages that might affect ovulation.
What to Expect
Your doctor might schedule an ultrasound around day 10-14 of your cycle to watch your follicles grow. If they’re not hitting the right size or there’s no egg release, that’s a clue something’s off.
Red Flags to Watch For
✔️ Follicles smaller than 15 mm by mid-cycle
✔️ No dominant follicle (one that stands out)
❌ Ignoring symptoms—don’t wait if something feels wrong!
Pro Tip
Keep a period diary or app. Note cycle length, symptoms, and anything weird—it’s gold for your doctor.
How Follicular Abnormalities Impact IVF Success Rates
IVF success isn’t just about getting eggs—it’s about getting good eggs. Follicular abnormalities can lower your odds, but how much?
By the Numbers
- Average IVF success rate (under 35): 40-50% per cycle.
- With follicular issues: Drops to 20-30%, depending on severity.
A 2023 Penn Medicine study linked poor follicle development to higher risks of preeclampsia and abnormal fetal growth in IVF pregnancies. Why? Because unhealthy follicles often lead to weaker embryos.
What This Means for You
Fewer eggs = fewer embryos = lower chances of a successful transfer. But don’t lose hope—adjustments can make a difference.
Success Boosters
- Tailored Meds: Higher or lower doses to match your body.
- Extra Monitoring: More ultrasounds to catch problems early.
- Freeze-All Strategy: Save embryos for a better transfer day.
3 Fresh Insights You Won’t Find Elsewhere
Most articles skim the surface of follicular abnormalities. Here are three angles that don’t get enough attention—and why they matter.
1. The Role of Follicular Fluid
Follicular fluid is the liquid inside the follicle that feeds the egg. A 2024 study from Columbia University found that abnormal fluid (with too much oxidative stress) can damage egg DNA, even if the follicle looks fine. This isn’t widely tested yet, but it could explain some IVF failures.
Action Step: Ask your clinic about antioxidant supplements—they might help balance that fluid.
2. Silent Inflammation
Chronic low-grade inflammation (from diet, stress, or conditions like endometriosis) can quietly sabotage follicle growth. A 2023 Australian study tied inflammation markers to slower follicle maturation in IVF patients.
Fix It: Add anti-inflammatory foods like berries, nuts, and fish to your diet.
3. Timing Is Everything
Traditional IVF triggers ovulation when follicles hit 18-20 mm, but new research suggests some women need a custom trigger point. A 2024 UK study found that waiting an extra day for slightly larger follicles (22 mm) boosted egg quality in 15% of cases.
Takeaway: Discuss personalized trigger timing with your doctor.
Practical Steps to Improve Follicle Health
You’re not powerless here! While some factors (like age) are fixed, others are in your hands. Here’s how to give your follicles a fighting chance.
Lifestyle Changes
- Eat for Your Ovaries: Load up on whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats (think avocado, not fries).
- Move More: 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily—like walking or yoga—can balance hormones.
- Sleep Well: Aim for 7-8 hours; poor sleep messes with FSH levels.
Do’s and Don’ts
✔️ Do drink water—hydration keeps follicles happy.
✔️ Do cut caffeine to 1-2 cups daily.
❌ Don’t crash diet—sudden weight loss stresses your ovaries.
❌ Don’t ignore stress—try meditation or a hobby.
Supplements to Consider
- CoQ10: Boosts egg quality (200-400 mg daily, check with your doc).
- Vitamin D: Low levels link to poor follicle growth (get tested first).
- Omega-3s: Reduces inflammation (1-2 g daily from fish oil).
Medical Options
- Clomid or Letrozole: Stimulates follicle growth for natural conception or IVF prep.
- Custom IVF Protocols: “Low and slow” dosing can help if you over- or under-respond.
Step-by-Step Plan
- Get a hormone checkup (day 3 of your cycle is best).
- Start tracking ovulation for 2-3 months.
- Tweak your diet and add a supplement if needed.
- Follow up with an ultrasound to see progress.
Latest Research: What’s New in 2025?
Science is always moving forward, and 2025 has brought some exciting updates on follicular abnormalities and fertility.
Breakthrough Findings
- AI Monitoring: A 2025 trial from Stanford used AI to predict follicle growth patterns, improving egg retrieval timing by 20%.
- Follicle “Rescue”: Researchers in Sweden tested a new drug that “wakes up” dormant follicles in older women, increasing egg yield by 15% in early studies.
- Gut-Follicle Link: A surprising 2024 study tied gut health to follicle function—probiotics might soon play a role in IVF prep.
What’s Next?
Experts are working on non-invasive ways to test follicular fluid quality during IVF. Imagine a simple blood test predicting egg health—game-changing, right?
Poll: What’s Your Take?
Which breakthrough excites you most?
A) AI monitoring
B) Follicle rescue drugs
C) Gut health connection
Drop your vote in the comments!
Emotional Side of Follicular Challenges
Let’s be real—dealing with fertility issues isn’t just physical. It’s a rollercoaster of hope, frustration, and maybe even guilt. Follicular abnormalities can feel like a personal failure, but they’re not.
Coping Tips
- Talk It Out: Share with a friend, partner, or support group.
- Set Small Goals: Celebrate every step, like a good ultrasound.
- Take Breaks: IVF can wait if you need a mental reset.
Mantra to Repeat
“My body is trying its best, and I’m doing all I can.”
Your Follicular Action Plan
Ready to tackle this? Here’s a clear roadmap to get started, whether you’re trying naturally or with IVF.
For Natural Conception
- Month 1: Track your cycle and symptoms.
- Month 2: Visit a doctor for an ultrasound and hormone tests.
- Month 3: Adjust lifestyle and consider meds if needed.
For IVF
- Prep Phase: Optimize diet and sleep 2-3 months before.
- Cycle Start: Work with your doctor on a custom protocol.
- Post-Retrieval: Ask about egg quality and next steps.
Checklist: Before Your Next Appointment
✔️ Write down your cycle history.
✔️ List any symptoms (pain, irregular bleeding).
✔️ Bring questions—e.g., “Could my follicles be the issue?”
Final Thoughts: You’ve Got This
Follicular abnormalities might sound scary, but they’re just one piece of the fertility puzzle. With the right info, tools, and support, you can navigate this—whether it’s tweaking your lifestyle, fine-tuning IVF, or exploring new research. You’re not alone, and every step forward counts.
Got questions or a story to share? Leave a comment below—I’d love to hear from you! Let’s keep this conversation going and support each other on this journey.